Today let’s speak about 3 different functions in infrastructure design and operation in simple words - DevOps, SysOps and SRE. Why you need all these functions and how Managed Service Providers can save your spendings on infrastructure.
DevOps
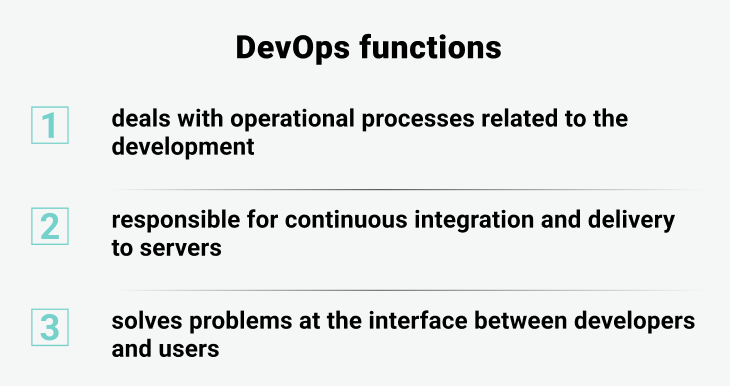
DevOps has changed the game over the past few years. Every organization, small or large, is adopting a DevOps culture today. Devops helps you automate everything and make things easier with faster and more efficient software deployment. It is a blend of culture and philosophy, practices and tools that helps organizations rapidly deploy services and applications. It improves and develops the product at a faster pace, instead of using traditional approaches to software development and infrastructure management.
In fact, DevOps work is a mix of practices and tools that help organizations deliver new services and applications more frequently. The advantage of these specialists is precisely in the multi-approach: they improve and develop the product at a faster pace already due to the fact that they do not use traditional approaches and “crutches” in software development and infrastructure management. In simple words, DevOps solves the problems that arise at the intersection of the work of developers and users.
Infrastructure as Code. Such specialists try not to change anything in the system manually, that is, they write scripts and configuration files for everything. What for? Yes, at least in order to reduce the likelihood of human error. In addition, this approach makes it easy to reproduce settings on other servers and find out exactly how the system is configured.
DevOps tooling is focused on building a convenient technological environment for creating products and testing hypotheses for these products. There are already ready-made ecosystems such as Amazon, GCP, Azure. There are tools that can be the basis for their own customizable ecosystem - Kubernetes, Ansible, Jenkins can be its components. Docker serves for packaging and standardizing knowledge on configuring and configuring an application.
Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)
The goal of an SRE engineer is to ensure that the service performs as reliably as specified in the Service Level Agreement (SLA). The stability of the work depends on both the infrastructure and the quality of the code, so SRE is engaged in both. As a rule, experienced system administrators or developers become SRE engineers. Developers even more often. At the same time, unlike most software developers, they write code not in order to implement business logic, but in order to increase the stability and performance of the system. That is, writing code is not the main task of an SRE engineer - it is just a way to achieve the main goal.
SRE specialists are a lifesaver for businesses. It is on the shoulders of the Site Reliability Engineering team that all sudden malfunctions and server crashes are assigned. In fact, this is one of the forms of DevOps implementation, but to deal with unplanned acute situations and ensure the stability of the application.
In addition, an SRE engineer can develop utilities to help monitor the system. For example, you already have tracing or log collection utilities on your project, but they do not suit the SRE engineer for some reason, but this is not a problem, because they can either write their own utilities or modify existing ones.

SysOps
Sometimes they refer to themselves as "operations engineers", "systems engineer", "infrastructure engineer". In the past, a "SysOps" or "Systems Operator" referred to any person who was in charge of any computer system, jack-of-all-trades or AnyKey specialist.The term can also be used to refer to the administrators of internet-based network services - with the development of cloud technologies, SysOps became responsible for multi-user systems.
Typical responsibilities include supporting the physical or cloud infrastructure, as well as related hardware and software. The infrastructure can be designed both for internal needs (for example, storing customer data, processing transactions), and for external needs - hosting a site, service, etc. To execute this function you need experience in deploying, scaling, migrating and managing systems, in particular cloud ones. SysOps follows the ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) approach. The focus here is on establishing strict rules for delivering IT services that are consistent with business goals.

Hiring all these functions will cost you significant money. But there’s always an easier road. You can prefer to hire an MSP - a Managed Service Provider. Basically, is a third-party company that remotely manages its clients’ hardware and software. This includes support of the servers, networks, cloud services, special software, and other systems. MSPs also handle infrastructure planning and setting, management of all IT processes and contractors if needed. Overall, it’s an all-in-one solution for those who are not ready to create their own IT department.
Get a free consultation on Managed Hosting or Full Server Maintenance.